When developing a link-building strategy, many digital marketers mistakenly prioritize backlinks over internal links.
While backlinks are valuable, internal links are the glue that connect your domain's pages, supporting site structure and offering context to search engines. The benefits of internal linking range from enhancing the user experience to improving engagement metrics.
Plus, your internal linking strategy is fully within your control — unlike external links.
However, there are still many challenges to internal linking at scale. This post will teach you the most common issues with internal links (and how to fix them!) so you get the most value from your links.
Key Takeaways
- Fix technical blockers first to ensure your critical pages are crawled, indexed, and discoverable.
- Build a logical, hierarchical link structure that reinforces topical depth and anchor-text clarity.
- Prioritize contextual relevance so internal links guide users and search engines through connected content.
Table of Contents:
Top Internal Linking Mistakes In Order of Priority
Some internal linking mistakes can have a large impact on your site's SEO success and organic visibility.
To help you prioritize your efforts, we've organized the most common internal linking issues into three categories (technical, site taxonomy, and relevancy problems) and laid them out by order of importance.
Priority 1: Technical Issues
The most common (and the most detrimental) internal linking mistakes deal with technical issues and implementation. Here are some frequent technical issues to look out for...
1. Orphaned Pages
Orphaned pages refer to pages that have no internal links pointing to them, isolating them from the rest of the site.
These pages often remain unseen because crawlers cannot easily reach them. They are especially frustrating because Google and AI search engines may not even index them!
To solve the problem of orphaned pages, regularly audit your site to identify pages without internal links and create relevant links to these pages from other high-traffic areas of your site. Implementing a system for continuous monitoring can help prevent future orphaned pages.
2. Too Many Links On a Page
Another common technical issue is having too many links on the page that is linking out. Too many links overwhelm users and reduce crawl efficiency for search engines. This wastes crawl budget and slows discovery of important site content.
The total number of links on a page include those in the body content as well as the links in the header and footer.
How many internal links is too many?
While there isn't a hard and fast limit on the number of internal links on a page (large ecommerce sites can get away with thousands), it’s generally recommended to stay in the range of 100 internal links on average to maximize the number of URLs crawled and followed.
The key is to avoid over-stuffing and ensure a good user experience.
TIP: Look at GA4 to review the links that no one clicks and consider removing them.
3. Unintended Noindex or Nofollow Tags In Your Crawl Pattern
Other common technical linking mistakes are unintended noindex or nofollow tags in your crawl pattern.
These mistakes prevent search engines from crawling pages or passing internal value correctly. Incorrect noindex tags hide important pages from appearing in search results. Nofollow attributes block crawlers from transferring authority through important internal links.
To fix unintended noindex or nofollow tags in your crawl pattern, audit your site's meta tags to identify and correct any mistakenly applied noindex or nofollow attributes. Ensure that critical pages are indexable and followable.
4. Pages Restricted By Robots.txt
Internal links only help when search engines can reach each linked destination page. Robots.txt can stop crawlers from accessing those URLs entirely. Blocked pages make internal links useless because crawlers cannot pass authority or context.
As such it's important to review and update your robots.txt file to ensure it isn't blocking important pages. Additionally, include these pages in your XML sitemap to guide Google's crawler.
Recommended Reading: Common Robots.txt Issues and How to Avoid Them
We recommend taking care of these technical issues before moving on to the next priority: taxonomy.
Priority 2: Site Taxonomy Issues
Other than technical issues, the most common problems with internal links deal with the hierarchy of the links and determining which links point where.
You can think of your links and your site taxonomy as a tree branching out.
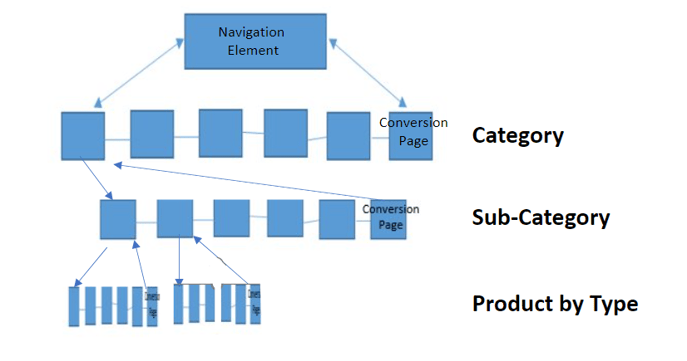
Following this visual, you should connect pages to each other that follow the same hierarchy (or branch), building out a link graph in a logical structure.
For sites with thousands of pages, optimizing an internal link structure poses a significant challenge. Fortunately, seoClarity's Link Seeker provides an automated solution that matches existing content with the most relevant pages on your site while still leveraging your input.
Paying attention to the site taxonomy also relates to the anchor text of the links. The common issue here is using the wrong anchor text, which is a missed optimization opportunity to tell the search engine what keyword you want a page to rank for.
It’s also recommended to avoid using the same anchor text for multiple pages.
Priority 3: Relevancy Issues
Once your pages and links follow a logical hierarchy, it's time to focus on relevance.
A common mistake is linking to irrelevant pages or those that don’t fit contextually. This can confuse users and dilute the value of your links.
Ideally, all relevant pages should be connected in a way that enhances the user experience, guiding visitors naturally through related content and making it easier for search engines to understand the structure of your site.
TIP: Classify your internal links by content type to organize them by topic. This allows you to create a circular reference where similar pages link together and connect back through the homepage.
Problem Solved: Internal Link Analysis at Scale
As you’ve seen, there’s a lot to consider when resolving internal linking mistakes. This is where SEO technology comes in.
Our Internal Link Analysis functionality, for example, assists with finding stops in your crawl pattern by identifying areas that contain nofollow, noindex, robots.txt or canonical to another page.
Those technical issues from priority 1 are already being solved!
Follow along our internal links workflow to gain more site authority.
You can also use it to identify the source of the internal link and next destination URL and any issues in the crawl patterns. This is more advanced than your typical internal links checker and a critical view to have if you’re going to actually fix them.
Returning to anchor text, the analysis can be used to review hyperlinks’ anchor text and locate similarities across multiple page types. If the anchor text is generic, you can go in and update it.
The view below shows a summary of the internal linking anchor text with the count of internal links that use it, and the count of unique pages that are linked by it.
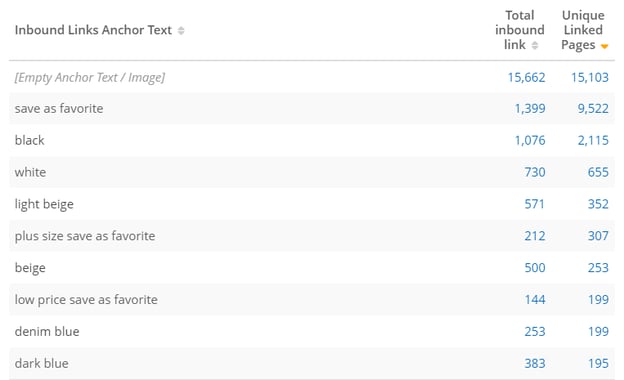
(Anchor text report in the Internal Link Analysis)
The analysis also allows you to review metrics that assist in weighting internal links and identify areas where internal links are not passing equity and value.
The functionality doesn’t end there! Receive intelligent recommendations that highlight all the pages where you should add links, and verify the relevancy with a link score.
SEO automation enters the conversation with the ability to have pages that mention a certain keyword or page automatically link to that mentioned target page. This immediately solves for orphaned pages!
Pretty cool, right? We’d love to give you a 5-day free trial to explore Internal Link Analysis and the rest of the seoClarity platform.
Summary
From resolving redirect chains and fixing broken internal links to ensuring contextual relevance, there are many internal linking mistakes to keep an eye out for.
But with the right SEO technology that can audit your linking structure, you’ll be able to provide a healthy experience to both users and search engines.
<<Editor's Note: This piece was originally published in July 2021 and has since been updated.>>









3 Comments
Click here to read/write comments