With organic search, you have many different metrics you can report on to share your progress with your team and executives.
Two of those metrics that are frequently used to evaluate content performance are average rank and weighted average rank.
Although both metrics have to do with rank position on the SERP, they are quite different from each other.
Here, we'll dissect both SEO metrics to see what they are, how they're calculated, and which is the better choice for you and your SEO rank reporting.
Table of Contents:
What is Average Rank?
One of the most popular metrics in SEO, average rank is simply the average of the rankings for the keywords you track for a day, week, or month.
How is Average Rank Calculated?
As an example, let’s say you track three keywords and their rank positions in the SERP for one day are 2, 21, and 4.
To find the average rank for these keywords, you would simply calculate the sum of the numbers and divide it by the number of integers.
In our example, the calculation would look like this: (2+21+4)/3
So in this case, the average rank for that given day is 9.
You can also calculate weekly or monthly average rank in two different ways, but doing so requires a few more steps...
One way is to calculate the best rank, where you select the highest rank for each keyword over the given time period (i.e. week or month). Then you calculate the average of those “best” ranks for each keyword.
It goes without saying that this method paints a positive picture since it only cares about the best keyword rankings.
Another option is to calculate the Mode (most frequently occurring) which – if you choose to use average rank at all – is the recommended method for finding out weekly and monthly average rank.
But reporting on average rank does have some downsides and, as you’ll see, is not the SEO metric that we recommend using.
The Downside of Average Rank
The biggest problem with average rank, and why we tend to tell clients to steer clear of it, is that it does not always reflect the true performance of a set of keywords over time.
As you saw above, the average rank workflow for a week or month can involve choosing the best rank per keyword, skewing the accuracy of the data set in a falsely positive light.
Another flaw in this method of rank reporting is that its calculation method treats all keywords as having the same importance.
In SEO, we know this is not true. Some keywords are more important than others due to weighing factors like higher search volume and larger demand.
A keyword with a search volume of 500 is much less important than a keyword with a search volume of, say, 20,000. Yet, with average rank, search volume isn’t even taken into account.
Let’s take a look at a visual example of this.
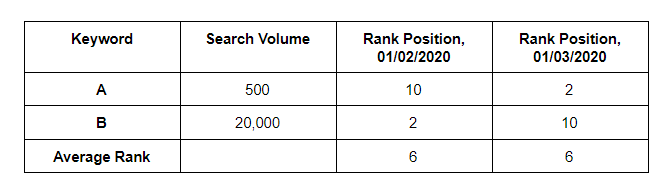
When you analyze the rankings for these two days using average rank as the metric, it would appear that nothing has changed since the average rank shown is the same (6).
But upon closer evaluation, you see that the rank decline (and the resulting impact on visibility and traffic) for keyword B would be much more substantial due to its high search volume.
Analyzing average rank does not highlight this negative change in rankings – which is why we recommend the use of another metric: weighted average rank.
What is Weighted Average Rank?
Unlike average rank, weighted average rank does not have the pitfall of treating all keywords the same.
This SEO metric gives each keyword a certain weight based on its search volume – the higher the search volume, the more important the keyword.
In other words, it carries a greater weight to impact ranking averages.
How to Calculate Weighted Average Rank
The first step to calculating weighted average rank is to find the weighted rank of each keyword. To do this, multiply the search volume of a keyword by its rank position.
Going back to our original example, this would look like:
500 x 10
500 x 2
20,000 x 2
20,000 x 10
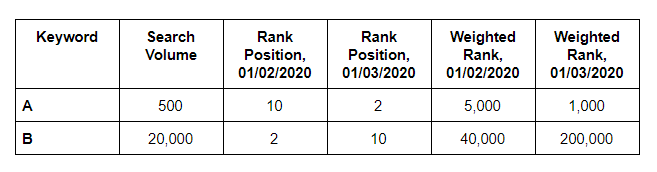
Now that you’ve calculated the weighted rank, the next step is to find the sum of the search volume and the sum of the weighted rank. The calculation for weighted average rank is then simply:
Sum of Weighted Rank/Sum of Search Volume
Let’s take another look at our example scenario, this time with an interest in the weighted average rank.
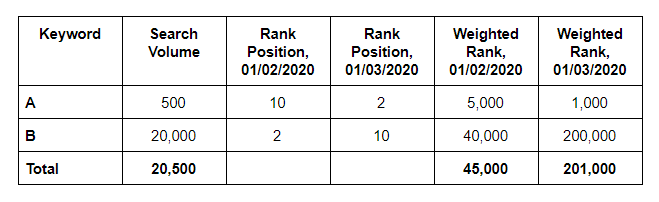
In this chart, we’ve found the sums for the search volume and the weighted ranks. Following the equation outlined above, we can now find the weighted average rank.
Weighted Average Rank, 01/02/2020 = 45,000/20,500 = 2.195
Weighted Average Rank, 01/03/2020 = 201,000/20,500 = 9.804
As you can see, the weighted average rank presents a much different number than the average rank did – for the same two days and keywords!
Remember: the average rank for both of these days was 6, which created no cause for concern. After all, nothing dropped, and nothing increased, so there was the false notion that nothing had changed.
When you take the weighting factor of search volume into account, however, you’ll see insights that aren’t available to you with just average rank.
The average rank position had a drop of 7.6 positions on the SERP.
As an SEO, seeing this data isn’t fun, but you can now analyze further and act on the information accordingly – information you’re only privy to if you analyze weighted average rank.
Average Rank vs. Weighted Average Rank: Which is Better For SEO Reporting?
As proven by the calculations above, weighted average rank is a much better metric to follow when compared to average rank.
By not taking into account search volume, average rank doesn't present an accurate representation of your rankings based on keyword importance. As a result, you could completely miss hugely impactful ranking changes for your most valuable keywords.
But with enterprise websites, manually calculating average ranks is just not an option – it takes up too much time. Time that could be used to actually execute your strategy instead of just forming it in the first place.
How to Determine Weighted Average Rank at Scale
To scale the process of calculating weighted average rank, use a proper rank tracker – it will reveal SEO metrics, including both average rank and weighted average rank for your tracked keywords.
At seoClarity, we have Rank Intelligence, which gives you accurate, reliable rank tracking and allows you to compare the two SEO metrics.
So let’s see how average rank versus weighted average rank leads to different analytics for tracked keywords over time.
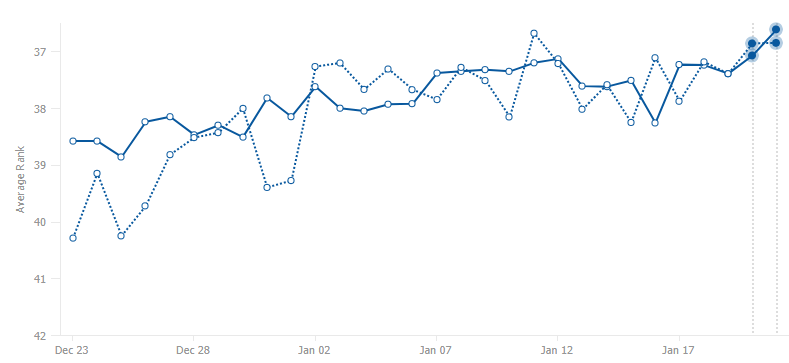
(Rank Intelligence view within the seoClarity platform.)
As you can see, the weighted average rank (dotted line) differs greatly from the average rank (solid line). It bears repeating that these differences exist because average rank is too surface level to properly capture the intricacies of SEO.
Look at December 25, for example. The average rank has a value of 38.8, while the weighted average rank for the same day has a value of 48.4.
If you were only to take into account the average rank, you would have a false idea of your rankings, because as the recommended metric (i.e. weighted average rank) shows, your rank position is actually 10 positions worse.
Closing Thoughts
Different SEO metrics present different information, and you must pay attention to the right data to see a true representation of your rankings.
Weighted average rank presents a more holistic view of rankings compared to average rank because it takes into account the weighting factor of keyword importance/search volume.
If we haven’t made this clear already: you should stop using average rank. For the purposes of SEO, it doesn't accurately present the information you need to report progress to executives and adjust your strategy accordingly.
If you stick with average rank, your SEO strategy will likely remain unchanged as well, which means never getting to the bottom of why the rankings are changing, and what you can do about it.
To learn more about how Rank Intelligence determines weighted average rank at scale, providing you with accurate information on your ranking performance, shedule a demo today!
<<Editor's Note: This piece was originally published in January 2020 and has since been updated.>>







Comments
Currently, there are no comments. Be the first to post one!